Simulation and animation of the dyanmics of a dice in a cup. The dice and the cup are initially suspended in the air when the simulation starts.
Skills Used:
- Python
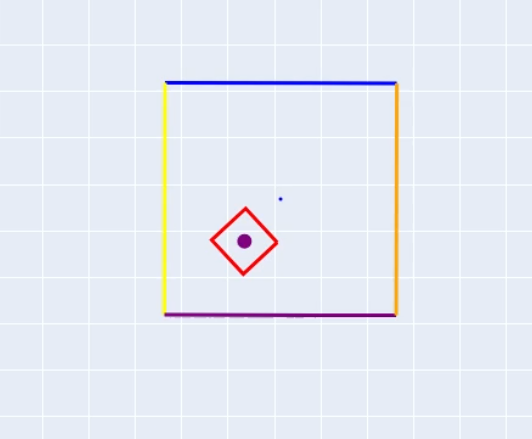
Initial Conditions
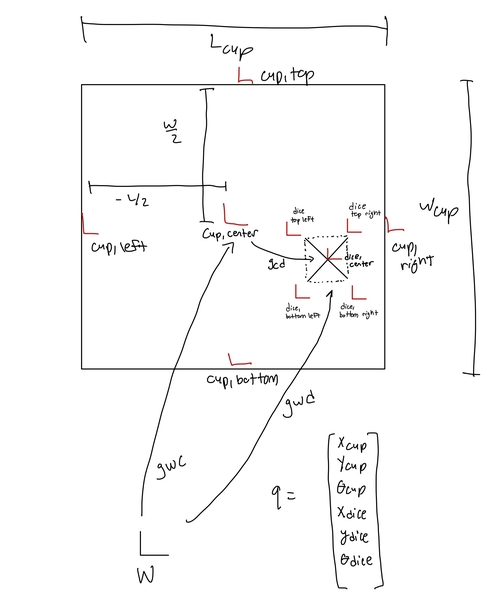
There are only 2 external forces acting on the entire system. There is a x and y force being applied only on the cup where the force acting on the x direction is a function of cosine to have oscillation in the system and the force in the y is there only to counteract the force of gravity of the cup. The y force prevents the cup from falling due to gravity. The dice has no external forces being applied and is only affected by gravity. There are 6 configuration variables and they are as the x,y and theta values for the both the dice and the cup.
Equations
To model the system, there are a few key equations that need to be calculated.
The first is kinetic energy for each item. Vb is the body velocity and I is the inertia tensor. Vb was calculated by applying transformations for both the cup and dice to get the locations of their center of mass’ in the world frame.
Next was potential energy. This was calculated by multiplying the mass of the dice and cup, respectively, by gravity and the y postiion.
Now with both PE and KE calculated, the Lagrangian can be calculated by subtracting the potential energy from the kinetic energy. The Euler Lagrange equations can now be found as well.
The impact equations can be found by subtracting the derivative of the Lagrangian with respect to the time derivative of the configuration variables before the impact from the same equation but after the impact. This will equal lambda multiplied by the derivative of phi, the contraint, with respect to the configuration variables. This will make up 6 equations, one for every configuration variable. The final equation for impact is the Hamiltonian which is the derivative of the Lagrangian with respect to the time derivative of the configuration variables multiplied by the time derivative of the configuration variables minus the Lagrangian.
It should be noted that dictionaries were made for before and after impact since numerically solving the equations would take far longer than solving symbolically. The velocities for both dictionaries are different since after impact, the velocities will be in the opposite direction but the position’s are the same.
Contraints
There are 16 constraints in this system. Each corner of the dice has four constraints. Those being the top wall of the cup, the bottom wall of the cup, the left wall of the cup and right wall of the cup. More specifically, the x component of the dice is compared to the right and left walls and the y component of the dice is compared to the top and bottom walls. 2 conditions for each corner of the dice is the x component plus or minus the length of the cup and the other two are the y component of the dice plus or minus the width of the cup. These four conditions for each corner of the dice results in the 16 constraints. This also results in each contraint corresponding to a phi equation.
Results
The simulation and animation both presented the expected behaviors for the system. As the simulation starts, the cup is moving only in the x direction and the dice starts to fall down. As the dice hits the bottom side of the cup, the dice bounces upward the cup starts to slowly move downward as some of the energy is being transferred to the cup that was not moving in the y axis at the start. Since the dice is continuously affected by gravity, it will keep going in the downward y direction and this results in the dice and cup system moving further down as time passes. The oscillating x force being applied on the cup results in the dice bouncing between the sides of the cup throughout the simulation.

The graph above shows when the dice impacts the cup when the velocities for the dice become negative. The whole system moves in the negative y direction as well.